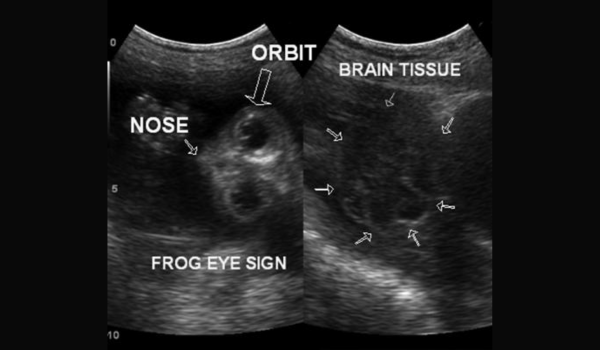
Neural tube defects (NTDs) affect thousands of babies globally and impair the brain and spine. We explore NTDs in detail in this blog, with a particular emphasis on two well-known varieties: anencephaly and spina bifida.
Neural tube defects (NTDs) are congenital deformities that occur in the early stage of embryonic development when the neural tube, which eventually forms the brain and spinal cord, fails to close properly. Various anomalies are caused by this condition, the most prevalent being anencephaly and spina bifida.
Neural Tube Defects – Spina Bifida and Anencephaly
Spina Bifida
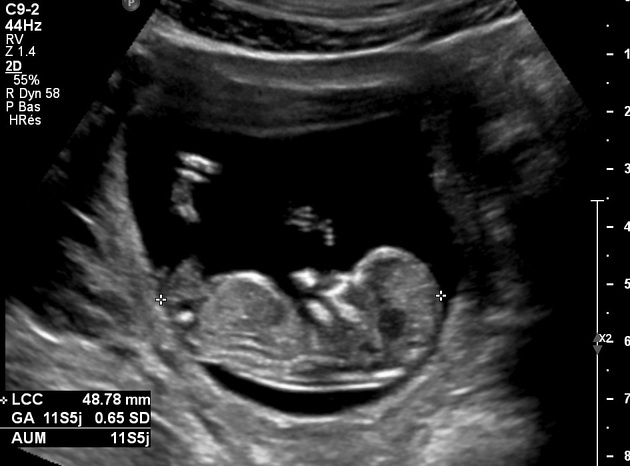
Spina bifida encompasses a spectrum of congenital anomalies affecting the spinal column. It occurs when the neural tube does not close completely during fetal development, leading to a gap in the spinal column. The severity of spina bifida can vary significantly, resulting in different types and degrees of disability.
The most common form is called myelomeningocele, where the spinal cord and its protective covering (meninges) protrude through an opening in the spine, forming a sac on the back. This condition can lead to paralysis, bladder and bowel dysfunction, and other neurological impairments.
Less severe variations include spina bifida occulta, in which the spinal cord is left intact and no visible signs are seen on the skin surface, and meningocele, in which only the meninges emerge through the spinal defect. However, even spina bifida occulta, can result in neurological problems such as limb weakness or numbness.
Anencephaly
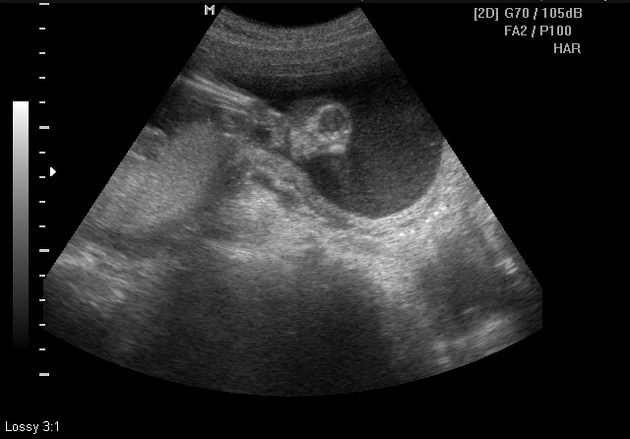
Anencephaly is a severe neural tube defect (NTD) marked by a significant loss of brain, skull, and scalp tissue. Because of the severe brain deformity, babies born with anencephaly usually do not survive long after birth. Usually, this condition causes a stillbirth or death soon after delivery.
The exact cause of NTDs like spina bifida and anencephaly is not entirely understood, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors likely plays a role. Folic acid deficiency during pregnancy has been identified as a significant risk factor for NTDs, emphasizing the importance of adequate prenatal care and nutrition.
Diagnosis and Management:
Spina bifida and Anencephaly are often diagnosed prenatally through careful ultrasound imaging or genetic testing. Early detection allows for timely interventions and management strategies, including surgical repair of the spinal defect, multidisciplinary medical care, and physical therapy.
With the advancements in fetal medicine and fetal therapy, it is even possible to correct the spinal defect during pregnancy itself which gives fairly good postsurgical outcomes. If the defect is severe with multiple other secondary effects, the couple can choose to terminate the pregnancy if detected within time. Unfortunately, there is no cure or effective treatment for anencephaly.
Prevention
While not all cases of NTDs can be prevented, there are some things that expectant mothers can do to reduce the risk. Folic acid supplementation before and during early pregnancy has been shown to significantly decrease the incidence of NTDs. Therefore, it is recommended that all women should consume folic acid daily, either through diet or supplements, to ensure adequate levels before conception and during the crucial early stages of pregnancy.
In Conclusion
Appropriate care and planning depend on early detection through diagnostic testing and prenatal screening. To correct the spinal deformity and stop further brain damage in cases of spina bifida, surgery may be necessary soon after delivery.
Parents must make difficult choices about end-of-life care and pregnancy management for pregnancies impacted by anencephaly. To assist families in navigating these difficult circumstances with compassion and understanding, genetic counselling and emotional support are essential.
Ongoing research aims to focus on the underlying genetic and environmental factors contributing to NTDs, with the ultimate goal of developing more effective prevention strategies and treatments. Advances in prenatal imaging techniques and surgical interventions offer hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for babies affected by these conditions.
To gain a deeper understanding of the matter and plan the subsequent actions, seek guidance from Dr Tejas Tamhane, a highly regarded specialist in fetal medicine based in Pune.
Neural Tube Defects Detection & Management in Pune
Consult Dr Tejas Tamhane, renowned Fetal Medicine Expert in Pune, to guide you through detecting and managing Neural Tube Defects (NTD) – Spina Bifida and Anencephaly.